Elevate Challenges in Enterprise Digital Transformation
What is a graph database?
A graph is a data structure used to describe network relationships between entities in the real world. A graph database, on the other hand, is an online data management system that operates semantically based on graph structures. It utilizes vertices (vertex) and edges (edge) to represent and store data, supporting operations for adding, deleting, modifying, and querying data.
Unlike traditional relational databases (RDBMS), graph databases store relationships directly. When performing relational queries, they do not require expensive and time-consuming JOIN operations with foreign keys as in relational databases. Compared to the traditional table structure storage model, this storage method in graph databases is more natural, focusing on the relationships between objects, providing an intuitive representation of the real world.
As the diagram below illustrates using Galaxybase graph database, it represents the relational connections between various entities such as directors, movies, actors, movie genres, and more.
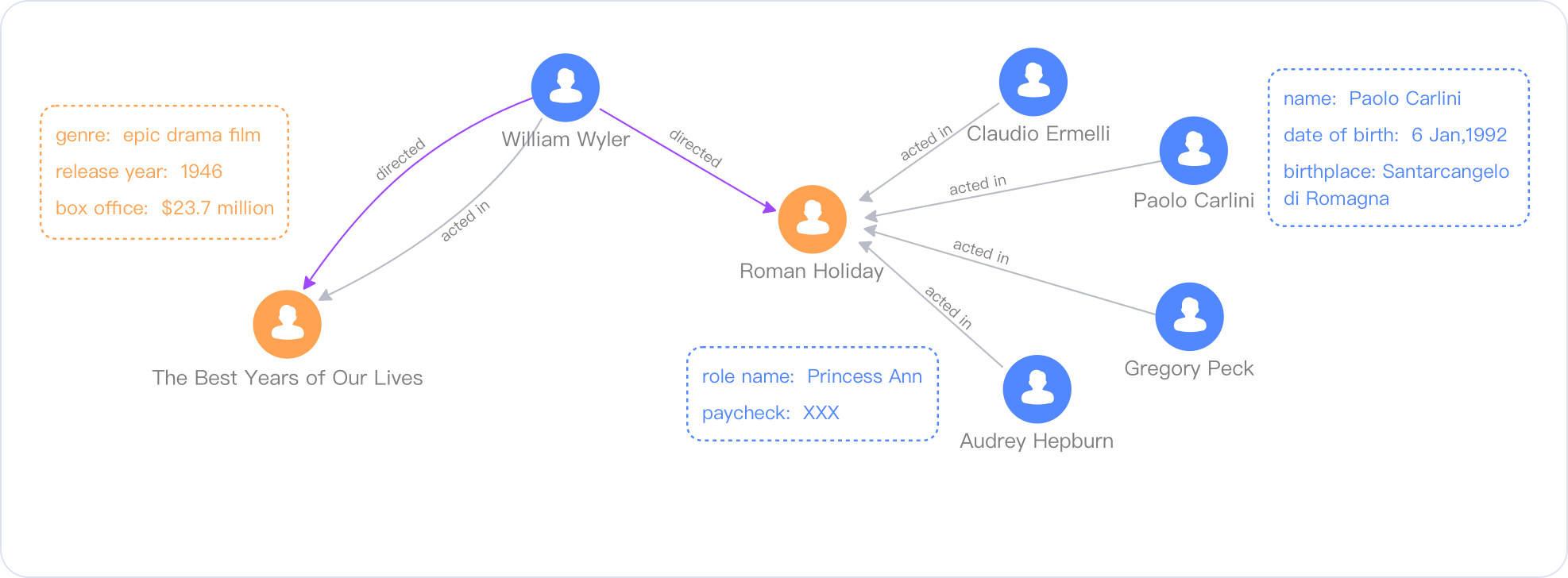
From a storage perspective, traditional relational databases store and manage data in a "two-dimensional table" format composed of rows and columns. In contrast, graph databases use nodes and edges as the fundamental storage units, designed for efficient storage and querying of graph data. Graph databases and relational databases share similarities with online transactional processing (OLTP) databases in supporting data manipulation operations (create, read, update, delete), typically accessed directly by applications.
Native Graph Storage

Completely Non-Native

Non-Native Storage





Get Started for Free

Business Consulting
400-882-6897
Pre-sales Consulting
0571-88013575
Enterprise Email
partner@chuanglintech.com
Media Cooperation
Marketing@chuanglintech.com
Address
Room 605, Building 6, No.666, Zhenhua Road, Sandun Town, Xihu District, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China